
Specialists in Engineering Metrology
|
|
How do laser interferometers work ? |
|
Interferometers use the interference of two light beams to perform relative measurements of displacement. The Agilent Laser Interferometer uses two known frequencies of laser light to take measurements. The two frequencies of light are split such that one of the frequencies follows a fixed path while the second frequency travels over the measurement path (figures 1 & 2).
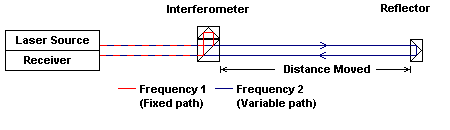
Figure 1. Path of Laser light in a basic interferometer
Stationary Interferometer Moving Reflector
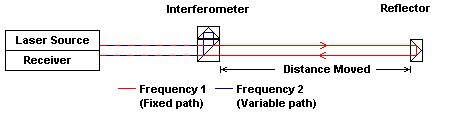
Figure 2. Path of Laser light in a basic interferometer
Moving Interferometer Stationary Reflector
When the two frequencies are recombined, a ‘beat frequency’ is obtained (figures 3 & 4). As the path length of the second frequency is changed the beat frequency changes. By measuring the beat frequency the distance moved can be calculated.
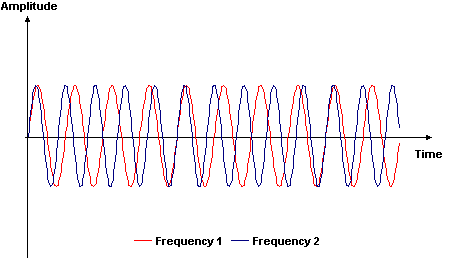
Figure 3. Two frequencies of light
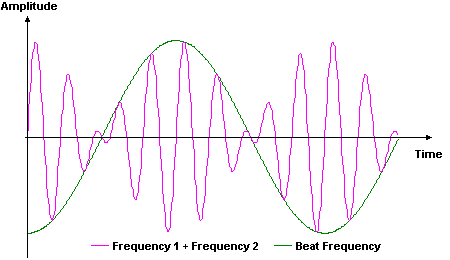
Figure 4. Interference of Frequencies 1 and 2 and the Beat Frequency
The simpler single frequency
interferometer works in a similar manner to that of the
two frequency system. Instead
of two frequencies, two beams of light of the same frequency are split such that
one of the light beams follows a fixed path while the second beam travels over
the measurement path. When these two light beams interfere the intensity varies
as the moving element causes the light path length to change. This method of
measurement is much more stable than single frequency systems when air
conditions are not perfect, such as can be expected when working on-site.
C. D. Measurements Ltd., Chomlea House, Hadfield Road, Hadfield, Glossop, SK13 2ER, U.K.
Tel. 01457 852929
Email : info@cdmeasurements.com
All Trade Marks Acknowledged